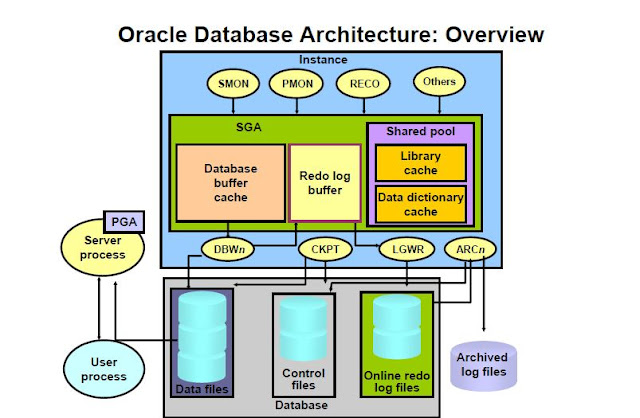
Oracle Database Architecture Overview
Oracle
Database
The general purpose of a database is to store and
retrieve related information.
Oracle database has a logical and physical structure
Physical
structure
The physical structure of database it’s the set of OS in
the database
It’s consist of three file types
Data
files:
Containing the actual data in database
Redo log files: Click hear
Record all changes made a data
It’s provide a recovery mechanism
Can be organized into groups
At least two groups are required
Control files: Click hear
Defines current status of physical database
At mount stage during startup
It’s a binary file
Memory
Structure
Oracle database consists of tow memory structure
System
Global Area (SGA):
It’s allocated at instance startup and other component of
an instance
Program
Global Area (PGA):
Allocated when the server process started
De allocated when process terminated
Used by only one process
System
Global Area (SGA):
It’s used to store the database information that is
shared by the database process
SGA consists of several memory structures
1) Shared pool
2) Database
Buffer Cache
3) Redo log
buffer
Shared
pool
Shared pool is store to most recently executed sql
statement and data definitions
It’ consists of two memory structures
Library
cache
Data
dictionary cached
Library
Cache
It’s stores information about the most recently used SQL
and PL/SQL statements
Enables the sharing of commonly used statements
Is managed by a least recently used (LRU) algorithm
Data
Dictionary Cache
A collection of most recently used SQL definitions in the
database
Includes information about database files, tables,
indexes, ect…
Size determined by the shared pool sizing
Database
Buffer Cache
Stores copy of data blocks that have been retrieved from
the data files
Redo log buffer
Records all changes made to the database data blocks
It’s primary purpose recovery
Oracle
database Background process
Database Writer:-
The Database Writer (DBWR) process is responsible for
writing dirty buffers from the database buffer cache to the datafile.
DB writer writing to the data files following events
occur
Tablespace offline mode
Tablespace Read only mode
Dropping or truncating a table
Tablespace begin and end backup
Checkpoint occurs
There are no free buffers
Log
Writer:-
LGWR performs sequential write from the redolog buffer to
the log file
Log writer writing the redo log files for following
events
Every committed transaction
When the redolog
buffer one third full
Every three seconds
Before DB writer writs
NOTE:
Redo log is need for recovery purpose. Log writer
conforms the commit operation after redo log is write
System
Monitor (SMON)
The
System Monitor Process (SMON) is the most critical background process for
Oracle Database. It performs critical tasks such as instance recovery, dead
transaction recovery and maintenance tasks such as temporary space reclamation,
data dictionary cleanup, and undo tablespace management.
SMON
performs many database maintenance tasks, including the following
Instance recovery
Instance recovery
Open database for user access
Rollback uncommitted transaction
Process
Monitor (PMON)
PMON is the process monitor it’s cleans up after failed
process by
Rollback the user's current transaction
Releasing the table or row locks
Releasing other resources.
Check
point (CKPT)
Checkpoints are recorded in the control file and each datafile
header, and are a crucial element of recovery.
When a checkpoint occurs, Oracle must update the headers of all datafiles to record the details of the checkpoint. This is done by the CKPT process. The CKPT process does not write blocks to disk, DBWn (DB Writer Process) always performs that task
The checkpoint process is responsible for updating file
headers in the database datafiles.
It’s synchronous the data
Log switch occurred
Updating data file headers with check point information
Updating control file with checkpoint information
Whenever manual log switch is done.
SQL> ALTER SYSTEM SWITCH LOGFILE;
Manual checkpoint.
SQL> ALTER SYSTEM CHECKPOINT;
Comments
Post a Comment